Melanobase
Table of Contents
NEW: check this screencast about MelanoBase published by the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics!
Short description
The main aim of the MelanoBase project is a large-scale automatic extraction of actionable information from the biomedical literature and its integration with existing structured knowledge (life science databases). The innovative outcome of this strategy is to provide users (basic and clinical researchers) with formats that can be more easily queried, and automatically processed, with the purpose of increasing the efficiency of biology research. The specific use-case scenario of melanoma disease has been selected for the histopathological complexity of these lesions, and to provide solutions for the unmet need of separating true drivers of this disease from a myriad of (epi)genetic inconsequential byproducts accumulated during melanoma genesis. The project will pursue a literature-wide and disease-centric approach which sets it apart from comparable projects worldwide. Moreover, close collaborations with experts in the field will streamline validation efforts in clinically-relevant specimens.
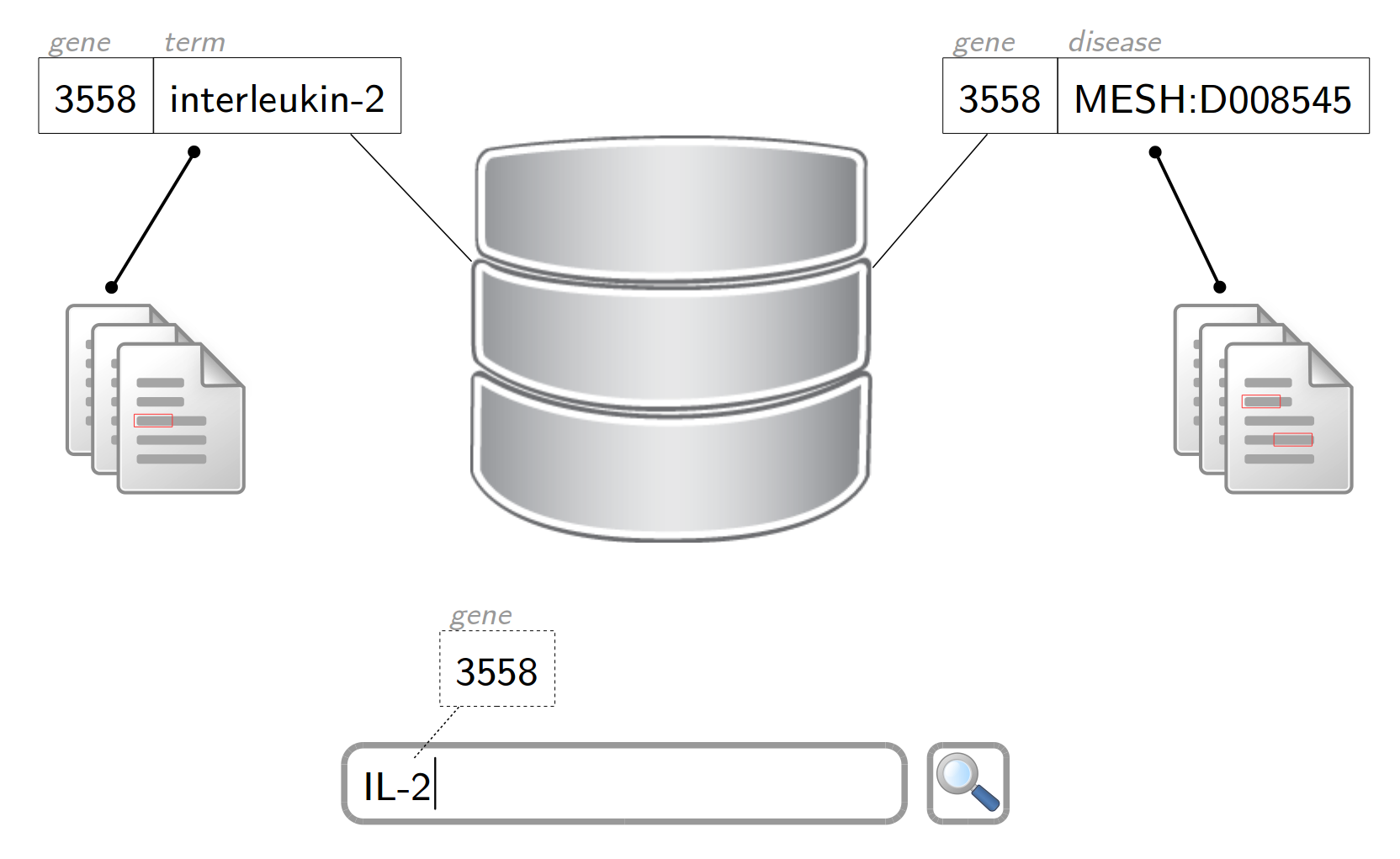
MelanoBase's vision: a conceptual index of the entire biomedical scientific literature, containing references to entities (eg. diseases, genes/proteins, chemicals) and relations as well as pointers to textual evidence.
External links
Major Publications
- Lenz Furrer, Joseph Cornelius & Fabio Rinaldi. Parallel sequence tagging for concept recognition. BMC Bioinformatics volume 22, Article number: 623 (2021). doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04511-y
- Roberto Zanoli, Alberto Lavelli, Theresa Löffler, Nicolas Andres Perez Gonzalez, Fabio Rinaldi. An annotated dataset for extracting gene-melanoma relations from scientific literature. Journal of Biomedical Semantics, volume 13, Article number: 2 (2022). doi: 10.1186/s13326-021-00251-3
- Ivano Lauriola, Fabio Aiolli, Alberto Lavelli, Fabio Rinaldi. Learning adaptive representations for entity recognition in the biomedical domain Journal of Biomedical Semantics, volume 12, Article number: 10 (2021). https://jbiomedsem.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13326-021-00238-0 doi: 10.1186/s13326-021-00238-0
- Nico Colic, Lenz Furrer, Fabio Rinaldi. Annotating the Pandemic: Named Entity Recognition and Normalisation in COVID-19 Literature. Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on NLP for COVID-19 (Part 2) at EMNLP 2020. doi: 10.18653/v1/2020.nlpcovid19-2.27
- Ellendorff, Tilia; Furrer, Lenz; Colic, Nicola; Aepli, Noëmi; Rinaldi, Fabio (2019). Approaching SMM4H with Merged Models and Multi-task Learning. In: Proceedings of the 4th Social Media Mining for Health Applications (#SMM4H) Workshop & Shared Task, Florence, Italy, 2 August 2019 - 2 August 2019, 58-61. doi: 10.18653/v1/W19-3208
- Vishnyakova, D., Rodriguez-Esteban, R., Rinaldi, F. (2019). A new approach and gold standard toward author disambiguation in MEDLINE. J Am Med Inform Assoc 26(10), pp. 1037–1045. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocz028
- Colic, N. and Rinaldi, F. Improving spaCy dependency annotation and PoS tagging web service using independent NER services. Genomics Inform. 2019;17(2):e21. doi: 10.5808/GI.2019.17.2.e21
- Furrer, Lenz; Jancso, Anna; Colic, Nicola; Rinaldi, Fabio (2019). OGER++: hybrid multi-type entity recognition. Journal of Cheminformatics, 11(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13321-018-0326-3
Datasets
We release the datasets created by the MelanoBase project as a publicly accessible resource on Mendeley: http://dx.doi.org/10.17632/745bpf597f.1
In particular the resource consist of:
- MGR base dataset (MelanoBase Gene Relation base dataset):
A dataset containing 907 papers annotated with text-level gene/melanoma relationship annotations (as opposed to document-level), reconstructed through a process of automated enrichment from a manually curated resource (MGDB). The publications are annotated at two levels: (i) entities of type gene and melanoma, and (ii) binary relations between genes and melanoma entities. This resource from the point of view of Melanoma research is basically equivalent to MGDB, but from the point of view of Natural Language Processing is a lot more useful, because it can be used to directly train and test automated extraction algorithms.
- MGR extended dataset (MelanoBase Gene Relation extended dataset):
A dataset of 2,657 distinct genes, potentially related to melanoma, automatically extracted from a pool of 89137 melanoma-related publications, using advanced algorithms trained on the MGR base dataset.
These resources and the process used for their creation are described in the following paper:
Roberto Zanoli, Alberto Lavelli, Theresa Löffler, Nicolas Andres Perez Gonzalez, Fabio Rinaldi. An annotated dataset for extracting gene-melanoma relations from scientific literature. Journal of Biomedical Semantics, volume 13, Article number: 2 (2022). doi: 10.1186/s13326-021-00251-3
Contact
E-Mail: fabio.rinaldi AT idsia.ch